Hash Function
A function that transforms any input into a fixed-length string of characters, uniquely representing the original data.
To put it in plain English
Works like a fingerprint for data: unique, tamper-evident, and impossible to reverse.
What is a hash function?
A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that converts any input data into a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash. The same input will always produce the same hash, but even the smallest change in input creates a completely different result.
Think of a hash like a digital fingerprint. Just as each fingerprint uniquely identifies a person, a hash uniquely represents data. Any small change to the data creates a completely different hash.
A hash function takes information and turns it into a short code that looks random. Change even one letter, and the code changes completely.
Why are hash functions important in blockchain?
Hash functions are the foundation of blockchain security and data integrity. They ensure that no one can alter a transaction or block without leaving visible proof.
Every block in a blockchain contains the hash of the previous block, creating a secure chain of records. If someone tried to change data in one block, its hash would change, breaking the link and alerting the network.
How do hash functions work?
When you run data through a hash function, it processes that data using complex mathematical rules to produce a unique hash value. The same data will always give the same hash, but the hash cannot be reversed to reveal the original input.
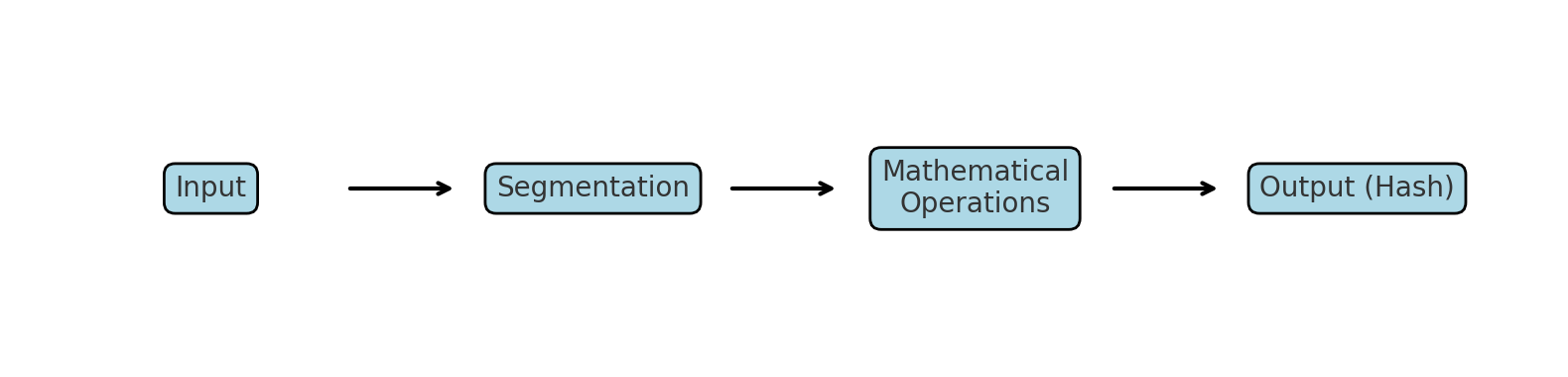
Here’s the step-by-step process:
-
Input processing: The hash function accepts an input (called a message), which can be of any size or format.
-
Segmentation: The input is divided into smaller, manageable parts.
-
Mathematical operations: Each part is transformed through a sequence of algorithmic steps.
-
Output: The results are combined into a single fixed-length value, the hash.
NOTE: Tools like Ethereum Transaction Decoder don't "decode" hashes in the cryptographic sense. Instead, they use the transaction hash as a lookup ID. You can look at it like using a tracking number to find a package. The actual transaction data (sender, receiver, gas fees) is stored on the blockchain, and the hash simply points to it.
Good hash functions have three important properties:
- Deterministic: The same input always produces the same output.
- Collision resistant: It is computationally infeasible (practically impossible with current technology) for two different inputs to produce the same hash.
- One-way: You cannot figure out the original input from the hash value.
Hash functions mix up data in a way that always looks random, but they follow consistent rules.
Types of hash functions
Different blockchain systems use different hash functions for speed, security, and design reasons. Here are two commonly used:
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit): Used in Bitcoin for mining and block creation. Also used in Solana's Proof of History (PoH) and transaction verification for speed and efficiency.
- Keccak-256: Used in Ethereum for generating addresses, hashing transaction data, and verifying smart contract interactions.
Blockchains use different kinds of hash functions, but all have the same goal: turning data into a secure digital fingerprint.
Using “hash function” in English
The term “hash function” appears in technical, business, and educational discussions about security and blockchain systems. Here are examples of how it’s used:
Technical Example
The blockchain uses a hash function to verify that each block has not been changed.
Business Example
Our platform uses hash functions to secure customer records and prevent data tampering.
Educational Example
In blockchain, a hash function acts like a digital fingerprint for every transaction.